URL vs URN vs URI
reading time
~ 4 min read
last Modified
published
Before going into the understanding of these three acronyms, we will learn what is the resource in the acronym of the URL, URN, URI .
URN - Uniform Resource Namespace
URL - Uniform Resource Locator
URI - Uniform Resource IdentifierWhat is Resource?
A resource can be HTML file, images, API endpoints, services, or any documents, books, research papers, etc.
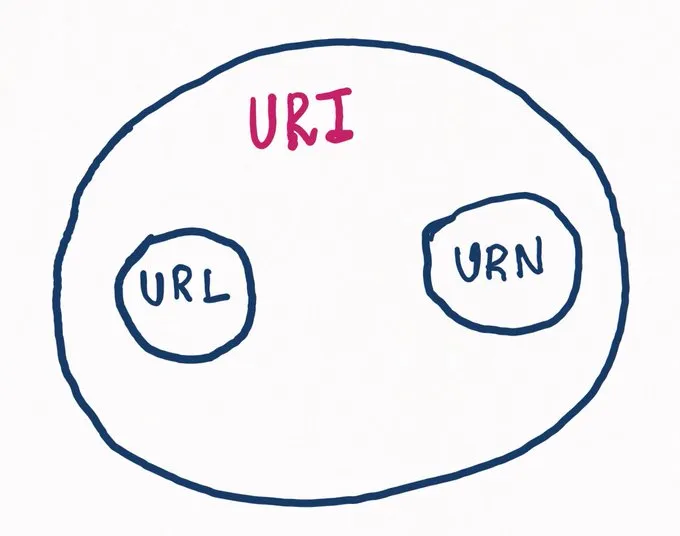
From the above diagram, we can able to see that URL and URN are the Subsets of URI (Uniform Resource Identifier). We will see what is URL and URN followed by URI.
URL
It is used to locate Specific resources on the web server or other. It knows where to find them.
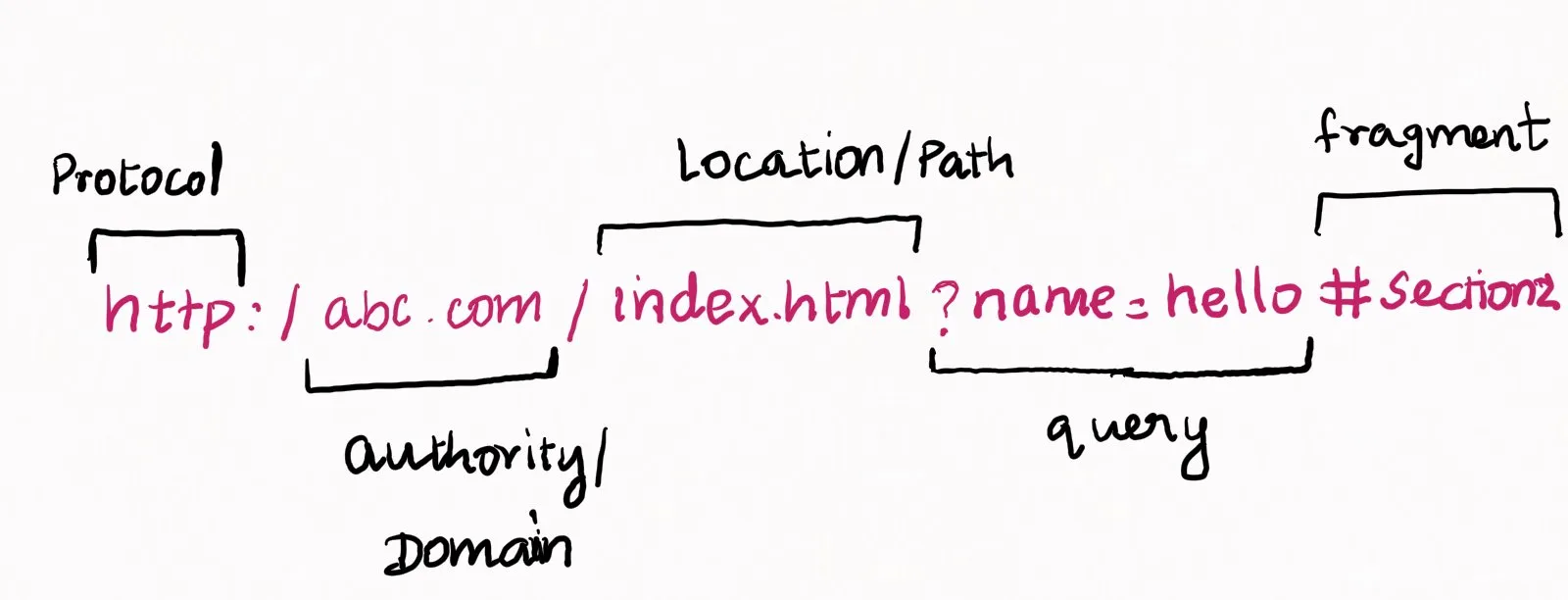
Syntax of URL
URL = Scheme/Protocol ":" Scheme_Specific_Path
where,
Scheme/Protocol = http,ftp,etc
Scheme_Specific_Path = path/to/retreival/of/resourceExample of the URL
URN
- it is the persistent labeling of the resources with an identifier. It does not imply where to find the resource. It is a globally unique name for the resources.
Syntax of URN
URN = "urn:" <NID> ":" <NSS>
where,
<NID> = NameSpace Identifier (case-insensitive, globally unique)
<NIS> = NameSpace Specific String (can contain query/fragments)Examples of URN:
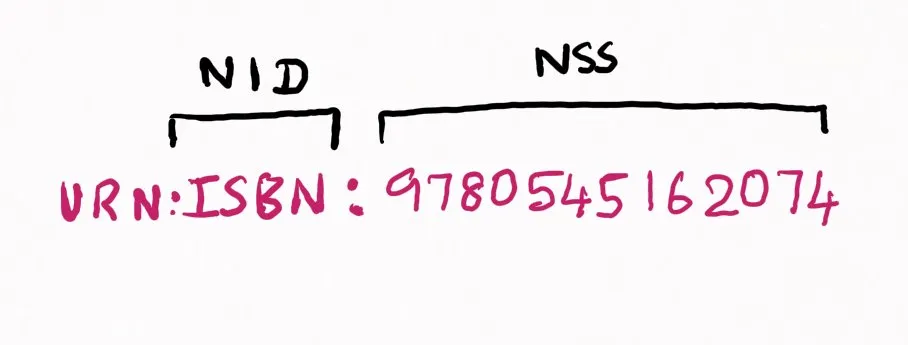
Here in the example, we can able to see ISBN is unique for the books and it just tells what is the ISBN id for the book rather than where to find them…
And from the above example, If we change the NID to
urn:isbn:9780545162074
urn:Isbn:9780545162074
urn:ISBN:9780545162074
urn:IsBn:9780545162074The above all are the same since it is case-sensitive
Check out other examples in wiki
URI
What is the common between these terms?? URN and URL follow the URI Syntax and it’s the subset of URI.
Syntax of URI
URI = Scheme : heir-part [? query] [# fragment]
where
- heir-part = authority or path (example.com / isbn:9780747532743)
- [? query] and [# fragment] are optional ones!From the above syntax, we can able to see the “Scheme” in the syntax matches with “scheme/protocol” in URL Syntax or “urn” in the URN Syntax.
Combining both of the above examples from URL and URN

we can able to distinguish that both URN and URL follow the URI Syntax.
Where we are using URI then??
In HTML,
<a href="uri scheme">SCHEME</a>the value of href can be http, ftp,mailto, urn, and other URI Schemes. It can be found on MDN , href supports URI Schemes which means we can do (“urn:isbn:0747532745”). And one of the common URI schemes we use “mailto:”… web browsers execute something called protocol handlers to handle the URI Schemes that are not HTTP/HTTPS.
code:
<a href="urn:mrn:iala:pub:g1143">URN</a>
<a href="mailto:[email protected]">mail</a>
<a href="ftp://speedtest.tele2.net">ftp</a>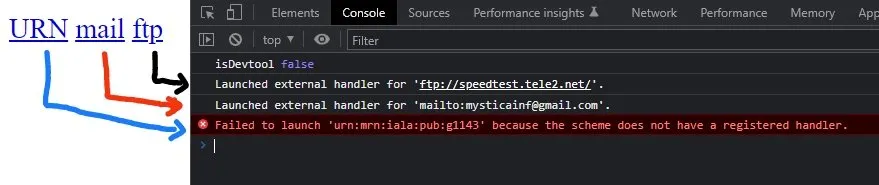 On running above html code, the browser console displaying URN as Failed to launch 'urn:mrn:iala:pub:g1143' because the scheme does not have a registered handle,for mail and ftp, it displays Launched external handler
On running above html code, the browser console displaying URN as Failed to launch 'urn:mrn:iala:pub:g1143' because the scheme does not have a registered handle,for mail and ftp, it displays Launched external handler In the above example, mailto: is one of the URI Scheme in which “mailto” will be scheme name and email id is the scheme path.
URN failed because the web browser can’t able to resolve the URN to URL…
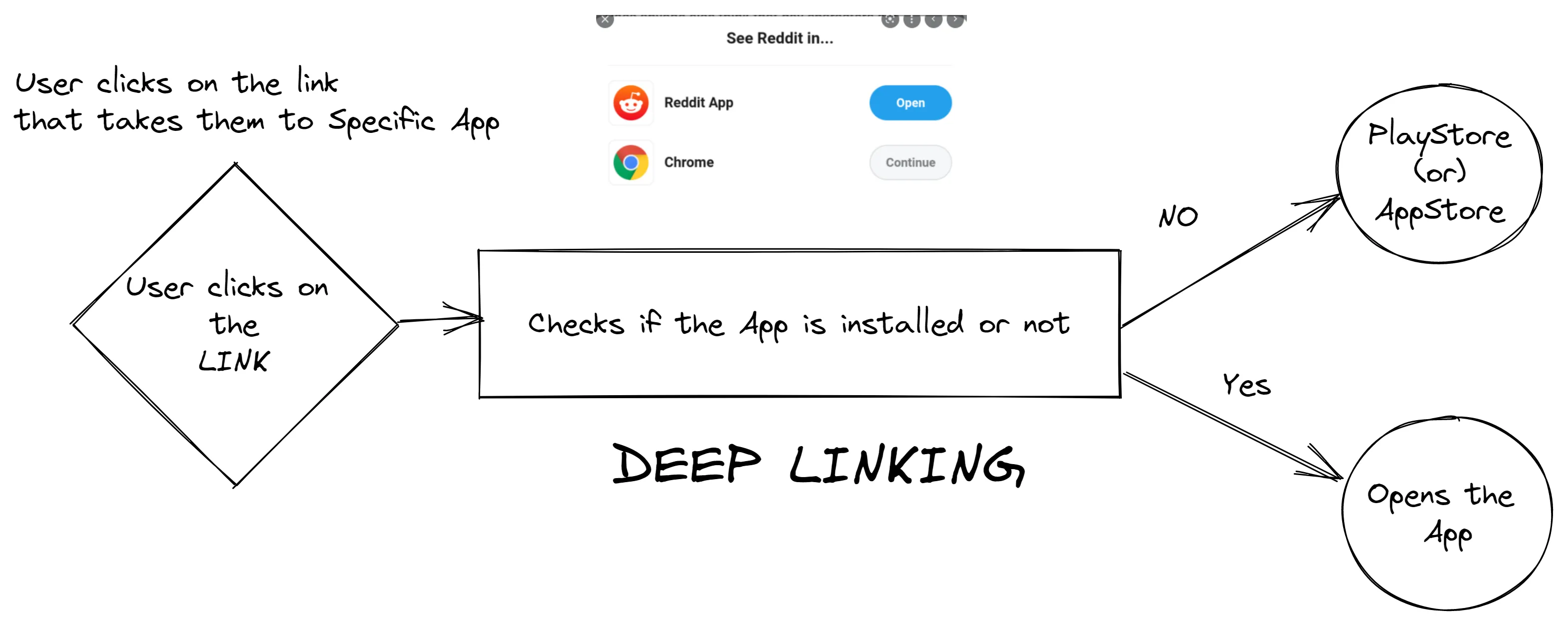
How URI Scheme works in mobile apps
Whenever you open a reddit on mobile browser, it asks whether to continue in web or switch to native app. Or some web site just switches to native app right away. That uses some form of deep linking.
Deep linking is technique to url/uri to link directly or specific content in the app. It can be done using custom uri schemes, app linking (android), universal linking (ios).
Here’s the list of URI Schemes for the apps link
reddit://
whatsapp://| URI Schemes | App Links (Android) or Universal Links (iOS) | |
|---|---|---|
| Format | Custom protocol (e.g., whatsapp://, myapp://) | Standard https:// URL |
| Fallback | No fallback (only works if app is installed) | Falls back to web if app is not installed |
| Security | Less secure (can be intercepted by other apps) | More secure (requires domain verification) |
| Handling | Opens the app directly if installed; no fallback | Opens app if installed, otherwise opens web page |
| Platform | All platforms (custom implementation) | Android/Ios only |
| Domain Verification | Not required | Required (app domain must be verified) |
| Example | myapp://section/page1 | https://example.com/product/12345 |
Nowadays, app links/universal links are preferred choice to avoid vulnerabilities. Since what if i register my application uri scheme with well-known uri like whatsapp:// and make the user to navigate to my app instead.
OAuth URI Schemes
Custom URI Schemes comes into play in real world when integrating OAuth into the application. OAuth providers (such as Firebase Auth,Supabase etc) use the redirect_uri parameter, which specifies a unique URI of the app. This URI allows applications to handle redirects from OAuth providers after user authentication.
TLDR;
- URL (location) starts with “protocol:”
- URN (namespace) starts with “urn:”
- URI - both URL and URN can be called as URI.